Website Scans
Select a website at top-left > Click 'Scan' in the top-menu > Open the ‘Website Scan’ tab.
- The website scan checks your front-end web-pages for vulnerabilities, errors and known malware. It is a good, ‘first-level’ check of threats on your site, but you should enable the full malware scanner for long-term protection.
- Website scan checks the following items:
- Javascripts, iframes and malicious links
- Safe browsing status (blacklist status)
- SSL certificate errors
- Content Management (CMS) errors
- HTTP errors and missing security headers
- The scan starts automatically right after you add a website
Run Website Scans and View Results
You can run a manual website scan every two hours and you can also schedule a website scan.
- Select a website at top-left then choose 'Scan'
- Open the 'Website Scan' tab
- Click 'Start Scan':
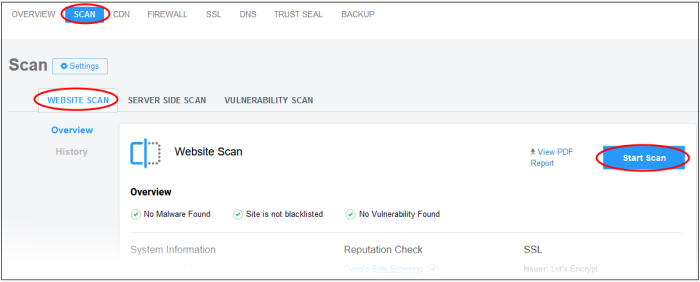
- The scan is added to tasks and may take a few minutes to complete:

- All vulnerabilities are shown at the end of the scan. The results show missing headers, SSL errors and blacklists on which your site appears:

- Request Cleanup - Create a ticket for Comodo security experts to fix all issues found by the scan. The link takes you to the support page where you can create a ticket.
- Malware Found - Click the 'Malware Found' link to start a deep virus scan of your web server. All malware will be removed at the end of the scan. Note – you need to configure the malware scanner if you haven’t yet done so. See 'Run Malware Scans and View Results' for additional information.
-
View PDF Reports - Click to view and download the scan report as a PDF.
- Site is blacklisted - The site was flagged as suspicious by Google’s ‘Safe Browsing’ service. Click the link to view the full reasons on Google's transparency report page.
- Vulnerabilities Detected - Security holes were found on your website. Click the link to run a CMS and OWASP Top 10 scan on the site. The results of these scans contain mitigation advice to help you fix the issues.
System Information
- Language - The programming language used in the site. For example, PHP, Python and so on.
- Web Server Extension - Optional module used in the website. For example, OpenSSL, mod_ssl, Google PageSpeed and so on.
- Font Scripts - Shows fonts used on your web pages.
- CMS - The content management system (CMS) tool used on the site.
- JavaScripts Included - Click the link to view details of JavaScripts used on site pages.
- Links Found - Click the link to view internal and external hyperlinks used on site pages.
- Iframes Included - Click the link to view internal and external inline frames (iframes) used in site pages. Iframes can be vulnerable to attack.
Reputation Check
- Google Safe Browsing - Opens https://transparencyreport.google.com/safe-browsing/. Use this site to check whether any of your sites have been flagged as harmful.
- Phishtank - Opens the PhishTank website at https://www.phishtank.com/. Use this site to run to see if any of your sites are listed as fraudulent.
SSL
- Issuer - The certificate authority that issued the certificate to your site.
- Expiration Date - Date on which the certificate expires. Please remember to replace certificates that are nearing expiry. Google Chrome and other browsers will show error messages to your visitors if your certificate is not valid.
- Warnings - Click the 'Issues found' / 'No issues found' link to visit https://www.sslshopper.com/ssl-checker.html. The checker runs a deep inspection of your SSL configuration and identifies any errors. The page also has plenty of remediation advice to help you fix any issues.
HTTP Security Headers
HTTP security headers are used to protect your website against attacks such as XSS, clickjacking, code injection and so on. SOCaaP Web Protection reports which security headers are missing from your site.



