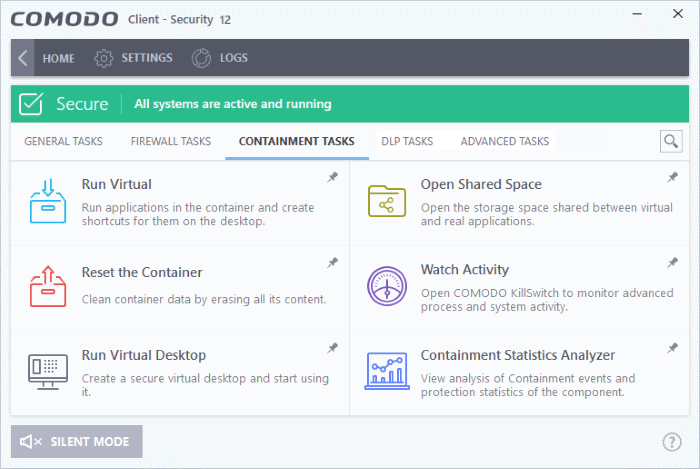
Containment Tasks - Introduction
- The container is a secure, virtual environment in which you can run unknown, untrusted, and suspicious applications
- Applications in the container are isolated from the rest of your computer. They are denied access to other processes, write to a virtual file system and registry, and cannot access your personal data
- This makes it an ideal environment for surfing the internet, because nothing you download can spread to your host system
- You can run applications in the container on an ad-hoc basis, and you can also create desktop shortcuts to always launch a program in the container
|
Note: Containment is not supported on Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 |
Containment tasks has the following areas:
- Run Virtual - Run individual applications in the container.
- Open Shared Space - Shared space is a folder which you can access from both your real desktop and the virtual desktop. When in the virtual desktop, save your files in shared space if you want to open them on your host computer.
Background. Applications in the container write to a
virtual file system and not your local drive. This prevents them
from making potentially malicious changes to your files and
folders.
The one exception to
this is a folder called 'Shared Space'. This folder can be accessed
by both your host operating system and contained programs. Use the
folder to share files between your computer and the container.
The
folder is located
'C:/Documents and Settings/All Users/Application
Data/Shared Space'.
- Reset Containment - Clears all data written by programs inside the container.
- Watch Activity - Open Comodo KillSwitch to identify unsafe processes and manage system activity.
- Run Virtual Desktop - Start the virtual desktop environment.
- Containment Statistics Analyzer - Detailed information about the processes running on your computer. Processes are split into contained and non-contained processes.
You might need to enter a password to access these tasks if so configured in the Endpoint Manager profile. See 'Password Protection' for more details.


